


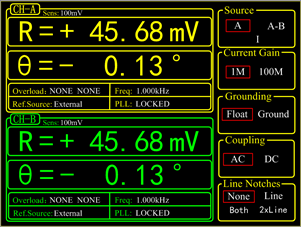
Input Channel
Two independent input channels have high synchronicity and can be individually configured as a single-ended mode or a differential voltage mode With the low-noise analog pre-amplifier, the signal input of OE1022D can be switched to operate in the single-ended or differential voltage mode, and the input noise is 5 nV/√Hz. The input impedance is 10 MΩ and the full-scale input voltage sensitivity ranges from 1 nV to 1V. Besides, OE1022D can also be used for current measurements with variable current gains of 106 or 108 V/A. Two line filters (50/60 Hz and 100/120 Hz) are designed to eliminate line related interference. The programmable gain amplifier is provided to adjust the dynamic reserve of the system according to the magnitude of the input signal, so that OE1022D has inherently large dynamic reserve up to 100dB. The sampling rate of 312.5KSPS is determined by a precision 24-bit A/D converter and a specific filter is designed to avoid aliasing.
Reference Channel
Two independent reference channels can work in external mode or internal mode. In internal mode, a precise and stable internal oscillator generates sine wave as an internal reference that is multiplied by the input signal. This internal signal is without any phase noise. With the digital phase-shifting technique, the phase resolution of the reference signal is 0.01 deg. OE1022D can work at any fixed frequency from 1 mHz to 102 kHz in this mode. In external mode, the reference signal can be a sine wave or a TTL pulse or a square wave. The rising or falling edge of the external reference signal triggers the Phase Lock Loop (PLL) to lock the external signal. Based on the frequency of the reference signal, the OE1022D can detect the harmonics of the input signal. The maximum harmonic signal frequency can reach 32767 times the fundamental frequency, and the maximum harmonic frequency cannot exceed the maximum operating frequency of the instrument by 102 kHz. In addition, the OE1022D has a single-channel reference mode, in which two independent input channels are locked and measured using the same external reference channel (REF IN A). This mode can further meet the need for higher synchronization requirements.
Display
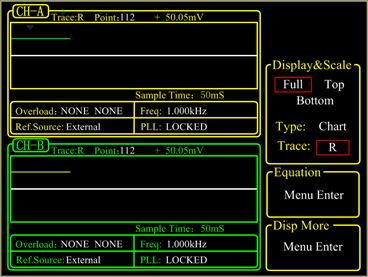
OE1022D uses the 5.6 inch 640×480 TFT color display as its screen. Data measured by OE1022D, such as, X, Y, R, θ, is stored in up to four traces. Trace values can be displayed as a bar graph or as a strip chart showing the trace values as a function of time.
Besides, OE1022D can display polar plots, showing phasor composed by in-phase and quadrature components of the signal. All displays can be easily scaled by the manual operation, and the auto-scale feature is available to optimize display quickly. The screen can be configured as a single large display, or two horizontally-split displays.
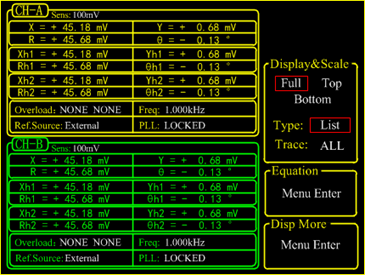
Simultaneous Multiple-harmonic Measurement
In the traditional lock-in amplifiers, only the fundamental frequency signal or a certain harmonic signal can be measured at one time, so it can not meet the requirement of multiple-harmonic measurement in some occasions. On the contrary, OE1022D uses a flexible digital framework combined FPGA and ARM, which make it practicable and efficient to measure 3 harmonic components simultaneously for each input channel, which means that each input channel is equivalent to three traditional lock-in amplifiers. Because of two independent input channels in OE1022D, OE1022D can detect 6 harmonics (2 fundamentals and 4 harmonics) at one time. The maximum harmonic signal frequency can reach 32,767 times the fundamental frequency, but the maximum harmonic frequency cannot exceed the maximum operating frequency of the instrument by 102 kHz.
Remote Operation
OE1022D uses RS-232 and USB 2.0 as standard interfaces. Through communication interfaces, all instrument functions can be controlled and all data can be read in real-time. Meanwhile, all interfaces of OE1022D are distributed on the front panel and the rear panel.
Dual Signal Channel
Voltage input Mode Single-ended or Differential
Full-scale Sensitivity 1 nV to 1 V in a 1-2-5 sequence
1 fA to 1 µA
Current input 106 or 108 V/A
Impedance
Voltage 10 MΩ
Current 1 kΩ to virtual ground
C.M.R.R >100 dB to 10 kHz, decreasing
Dynamic reserve >120 dB
Gain accuracy 0.2% typ, 1% max
Voltage Noise 5 nV/√Hz at 997 Hz
Current Noise 5 fA/√Hz at 97 Hz
13 fA/√Hz at 997 Hz
Line filters 50/60 Hz and 100/120 Hz
Gounding BNC shield can be grounded or floated via 10 kΩ to ground
Dual Reference Channel
Input
Frequency range 1 mHz to 102 kHz
Reference input TTL or Sine
Input impedance 1 MΩ
Square reference level VIH>3V, VIL<0.5V
Sine reference signal >1 Hz
> 400 mVpp
Phase
Resolution 0.001°
Absolute phase error <1°
Relative phase error <1 mdeg
Phase noise Internal ref. Synthesized, <0.0001 deg at1 kHz
External ref. 0.001 deg at 1 kHz (100 ms time constant, 12 dB/oct)
Drift <0.01 deg/℃ below 10 kHz
<0.1 deg/℃ above 10 kHz
Harmonic detection 2F, 3F, …nF to 102 kHz (n<32,767)
Acquisition time Internal Ref. Instantaneous acquisition
External Ref. (2 cycles + 5 ms) or 40 ms,whichever is larger
Demodulator
Number of demodulators 6
Stability
Digital outputs no zero drift on all setting
Display no zero drift on all setting
Analog outputs <5 ppm/℃ for all dynamic reserve settings
Harmonic rejection -90 dB
Time constants 10 µs to 3 ks (<200 Hz)
10 µs to 30 s (>200 Hz)
Synchronous filters Available below 200 Hz(18, 24 dB/oct rolloff)
Internal Oscillator
Frequency Range 1 mHz to 102 kHz
Accuracy 2 ppm + 10 µHz
Resolution 1 mHz
Disrortion -80 dBc (f<10 kHz),-70 dBc (f>10 kHz)
Amplitude 0.001Vrms to 5 Vrms ( Resolution:1 mVrms)
Accuracy 1%
Stability 50 ppm/℃
Sine Outputs Sine signal,output impedance 50 Ω
TTL Outputs 5V TTL/CMOS level,output impedance 200Ω
Display
Screen 5.6 inch, 640×480 TFT
Screen format Single or dual display
Display quantities Each display shows one trace,
traces can be defined as X,Y,R,θ
Display types Numerical form, bar graph, polar plot and strip chart
AUX Inputs and Outputs
CH1 and CH2 Outputs
Function Output X, Y, R, θ
Output Voltage ±10 V full scale.
30 mA max output current
Update Rate 312.5kHz
AUX Inputs
Function 4 Channel Inputs
Amplitude ±10 V,1 mV resolution ratio
Impedance 1 MΩ
AUX Outputs
Function 4 Channel Outputs
Amplitude ±10 V,1 mV resolution ratio
Drive current ±25mA max
Trigger Input
Function TTL external trigger is used for data storage
Monitor Output
Function Analog output of a signal-amplifier
Drive current ±40mA max
Interfaces
USB2.0
RS232 interfaces
IEEE-488 interface(optional)
General
Power requirements
Voltage 220-240 V AC
100-120 VAC(optional)
Frequency 50/60 Hz
Power 30 W
Power supply rejection 70dB@1MHz
Weight 11 KG
Dimensions
Width 448 mm
Depth 513 mm
Height
With feet 148 mm
Scanning Microscope AFM、STM、SPM
Materials Science Carrier mobility, Carrier density, Hall effect, Ultrasonic materials
Transport Measurement Conductivity measurement, Impedance measurement
Noise Represents Noise density, Cross-correlation measurement
Optical Experiment Spectral analysis, Spectral measurement, THz measurement, TDLAS
Sensor Measuring Gyroscope, Photoelectric sensor, Resonator, Accelerometer
Magnetic Sensor SQUIDs, NV color center, Atomic Magnetometer, VSM
Biomedical Microfluidic
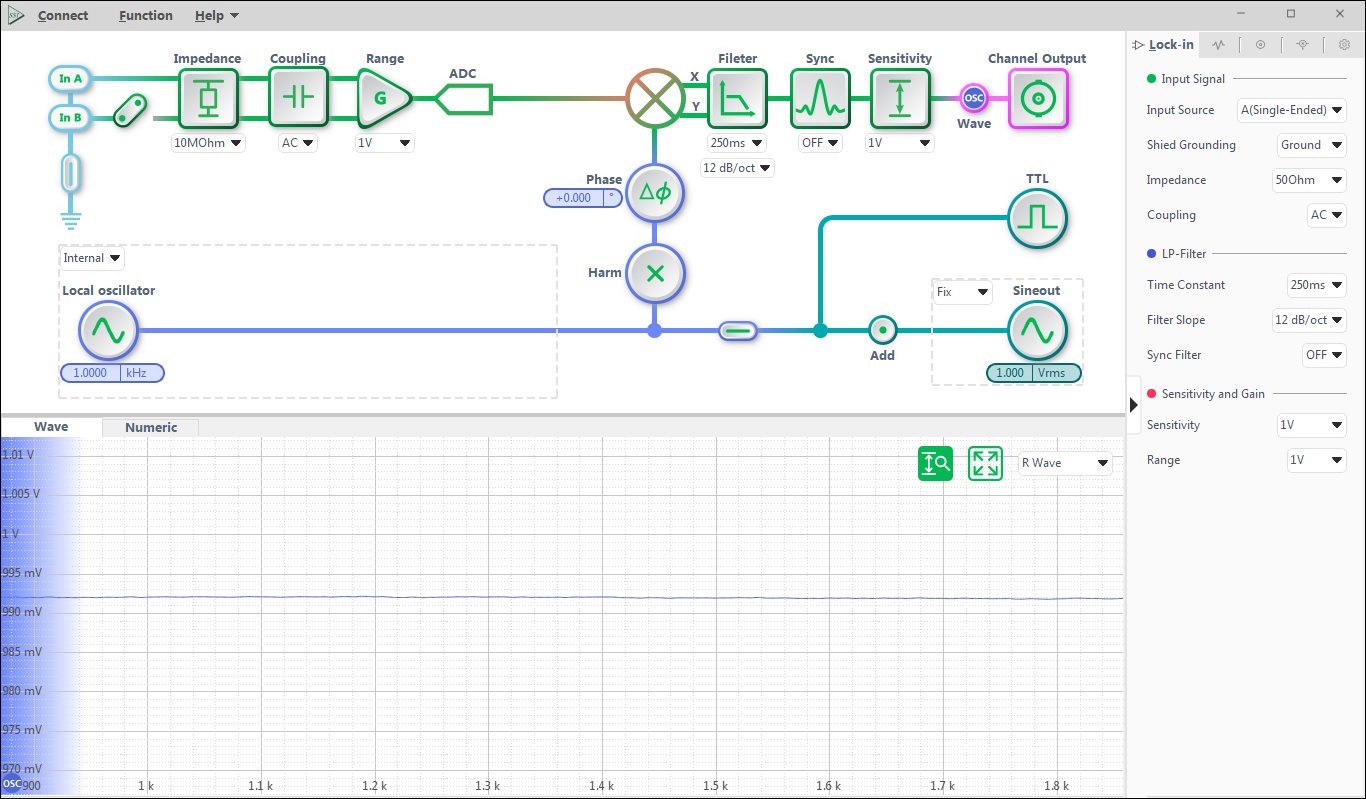
Lock-in Amplifier
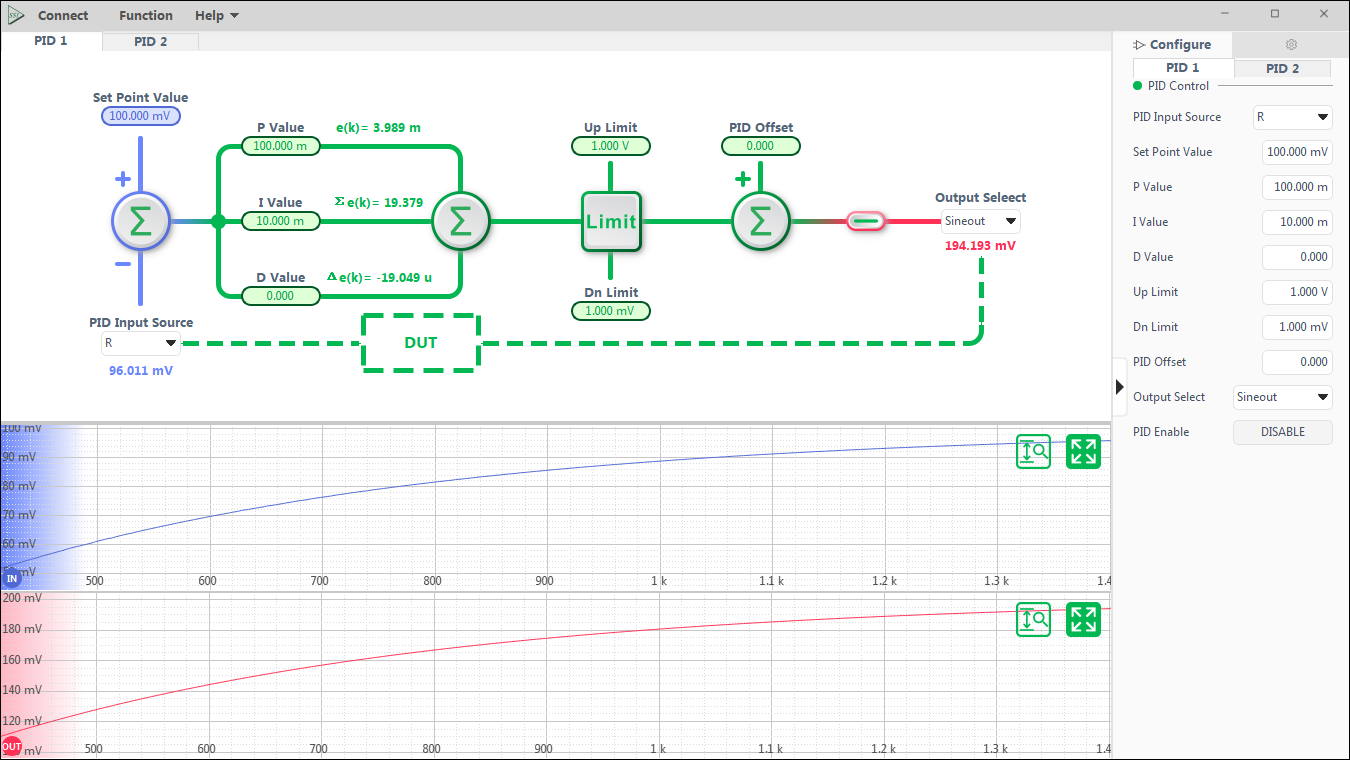
PID Controllers
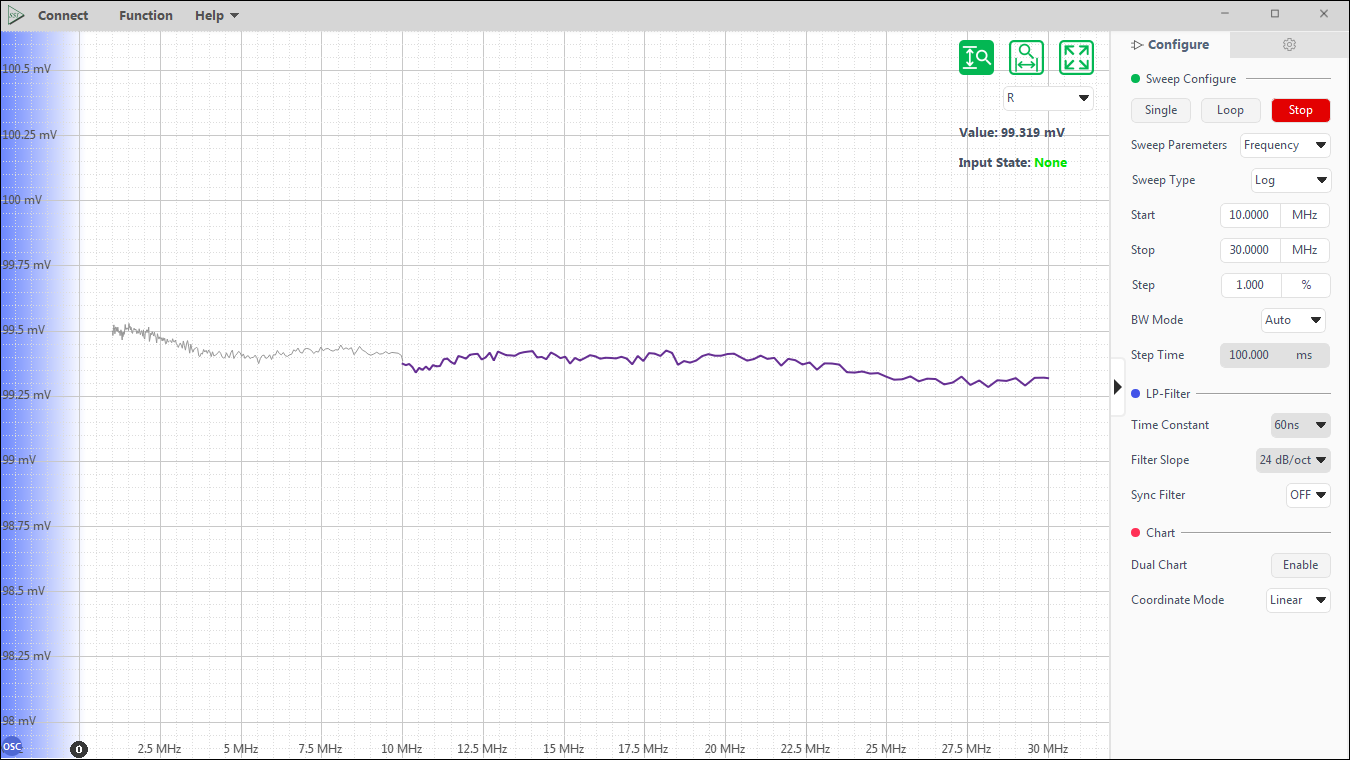
Parametric Sweeper
RS232 to GPIB Module
Optional RS232-GPIB conversion module, compatible with the RS232 interface of all Sanex Instruments products.